Scaling AI Workloads: Azure Best Practices
Practical strategies to scale AI workloads on Azure—use Spot VMs and reservations, autoscale with AKS and Azure ML, tune GPUs and secure deployments.

Scaling AI workloads on Azure can be simplified with smart strategies for cost control, performance optimisation, and resource management. Azure’s pay-as-you-go pricing, Spot VMs, and tools like Azure Machine Learning (Azure ML) and Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) make it a strong choice for businesses managing dynamic AI demands. Key takeaways include:
- Cost Savings: Use Spot VMs for up to 90% savings on interruptible tasks and Reserved Instances for predictable workloads.
- Resource Optimisation: Scale resources dynamically using auto-scaling, horizontal scaling (VM Scale Sets), and vertical scaling with GPU-optimised VMs.
- Simplified Management: Tools like Azure Data Lake, Blob Storage, and prebuilt AI models reduce complexity, while Azure Monitor ensures performance tracking.
- Security and Reliability: Ensure uptime with availability zones and secure data with encryption, RBAC, and private networking.
Azure helps businesses balance performance and costs, making AI workloads scalable without requiring deep expertise. Read on for detailed strategies to scale effectively.
Scaling your AI/ML practices with MLOps and Azure Machine Learning | Part 3
Azure AI Architecture Design Principles
Designing an AI architecture on Azure demands a focus on reliability, security, and cost management. To ensure uptime during failures, implement redundancy using availability zones or multi-region setups. This way, even if a data centre goes offline, your system remains operational. Security should be embedded from the outset - use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to manage permissions and private networking to safeguard sensitive components like inference server node pools in Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS).
A stateless design is key for smooth scaling. Stateless applications eliminate bottlenecks and make scaling straightforward. For cost control, reserve GPUs exclusively for AI workloads and benchmark to select the right VM SKUs. Storage should follow a "write once, read many" approach, which is efficient for AI workflows.
"AI workloads can be expensive, and costs can escalate quickly if resources aren't shut down, scaled down, or deallocated when they're not being used." - Microsoft Azure Well-Architected Framework
Choosing the right pricing model is critical. While pay-as-you-go is ideal for testing and experimentation, Provisioned Throughput Units (PTUs) provide consistent performance for production environments.
"For Azure OpenAI use cases that require Predictable, Consistent, and Cost Efficient usage of the service the Provisioned Throughput Unit (PTU) offering becomes the most reasonable solution especially when it comes to business-critical production workloads." - Manoranjan Rajguru, Microsoft
These principles lay the groundwork for building robust AI systems with Azure.
Core Components: Azure Machine Learning and Azure Kubernetes Service
Azure Machine Learning (Azure ML) and Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) form the backbone of many AI architectures. Azure ML handles model training, versioning, and tracking lineage, while AKS provides the computing power to deploy these models as scalable web services. This combination is highly effective - AKS can scale up to 5,000 nodes and 200,000 pods per cluster with Azure CNI Overlay, making it capable of managing demanding workloads.
For resilience, deploy models in AKS using Availability Zones. AKS also supports autoscaling, which works seamlessly with Azure ML online endpoints to adjust capacity based on live demand. This is especially important given that 99% of organisations face challenges in scaling AI workloads, and only 33% of leaders feel their teams are adequately skilled in AI.
To optimise resource use, configure training clusters to scale down to zero nodes when idle. Keep experimentation and production in separate workspaces to protect live systems while allowing innovation to continue safely.
Data Storage: Azure Data Lake and Blob Storage Integration
For high-volume AI data processing, Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 is a top choice. It supports structured data (SQL), semi-structured formats (like JSON and Parquet), and unstructured content (such as images and documents). Pairing this with Delta Lake enables features like data versioning and ACID transactions.
AI workloads often require handling massive data loads - up to 10 terabytes daily. This makes strong parallelisation capabilities essential. For simpler storage needs or tiering, Azure Blob Storage serves as a practical complement.
Security is paramount. Use platform-level encryption (either Microsoft-managed or customer-managed keys), Private Link for network isolation, and managed identities for secure authentication. Avoid direct access to data stores from AI code; instead, route requests through an API or data access layer to enforce authorisation and maintain user context. For governance, Microsoft Purview can help maintain a data catalogue and track data lineage across various sources.
Resource Scaling Strategies on Azure
Scaling AI workloads effectively means finding the right balance between performance and cost. Azure provides three main strategies for scaling: horizontal scaling (adding more instances), vertical scaling (boosting instance power), and auto-scaling (adjusting resources dynamically based on demand). Let’s dive into each method to understand how they can help manage resources efficiently on Azure.
Horizontal Scaling with Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets
Horizontal scaling involves adding more virtual machine (VM) instances to handle increased workloads, improving both system reliability and capacity. Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets (VMSS) simplify this process, especially when using Flexible orchestration mode, which supports a mix of different VM types within a single scale set. This flexibility is particularly useful for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) running varied AI workloads that require different compute capabilities.
For horizontal scaling to work well, AI applications should be designed as stateless, allowing any instance to process incoming requests. Automatic repair mechanisms can replace unhealthy nodes without manual intervention, ensuring smooth operations. Additionally, standby pools can prepare pre-allocated instances to handle sudden demand spikes.
Cost management is a key consideration. Setting the minimum node count to 0 ensures no charges accrue when no AI jobs are running. To further enhance resilience, distribute instances across multiple availability zones, ensuring continued operations even if one zone experiences issues.
| Scaling Component | SMB Benefit | Recommended Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum Node Count | Cost Elimination | Set to 0 for idle periods |
| Orchestration Mode | Management Flexibility | Flexible Mode |
| Instance Type | Cost Optimisation | Mix of Regular and Spot VMs |
| Storage | Performance | Ephemeral OS Disks |
| Scaling Trigger | Efficiency | Metric or Schedule-based |
Vertical Scaling Using GPU-Optimised Instances
Vertical scaling involves upgrading to larger, GPU-optimised VM sizes, making it ideal for resource-heavy tasks like model training and fine-tuning. This method is particularly effective when a single, powerful instance can outperform multiple smaller ones.
"GPU SKUs are expensive, so continuously monitor for under-utilisation and right-size resources as needed." - Microsoft Azure Well-Architected Framework
For intensive tasks such as training large transformer models, GPU compute like the NC-series is a strong choice. These models often require substantial memory - for instance, a transformer model with a batch size of 512 and context length of 2,048 can require 3TB of KV cache, roughly three times the model size. Selecting the right GPU SKU is therefore critical.
To optimise costs, Azure Reserved VM Instances offer discounts of up to 72% for one- or three-year commitments. For batch jobs that allow checkpointing, low-priority VMs provide access to surplus capacity at reduced prices. Additionally, idle shutdown policies can reduce expenses, and provisioning GPU compute in the same region as your data storage can lower network latency and transfer costs.
Auto-Scaling Configurations in Azure Machine Learning Workspaces
Auto-scaling takes resource management a step further by dynamically adjusting based on demand. For Azure Machine Learning compute clusters, setting the minimum node count to 0 ensures no charges are incurred when jobs aren’t running. The default idle time before scaling down is 120 seconds, but this can be reduced for non-iterative tasks to cut costs or extended for iterative development to minimise scaling overhead.
"To avoid charges when no jobs are running, set the minimum nodes to 0. This setting allows Azure Machine Learning to de-allocate the nodes when they aren't in use." - Microsoft Learn
For managed online endpoints delivering real-time inference, you can implement metrics-based scaling, such as triggering additional resources when CPU usage exceeds 70%, or schedule-based scaling for predictable peak periods. To avoid constant fluctuations, set clear thresholds - for example, scale out at 80% CPU usage and scale in at 60%. Additionally, early termination policies like Bandit or Median stopping can help optimise hyperparameter tuning by halting underperforming runs, saving valuable compute hours.
Performance Tuning Techniques for AI Workloads
After scaling, fine-tuning your AI workloads is crucial to strike the right balance between throughput, latency, and cost efficiency. These adjustments build on earlier scaling efforts, aiming to optimise resource use. Two areas stand out for improvement: data pipeline performance and monitoring.
SMB Multichannel for Azure Files in AI Data Pipelines
Slow data transfer can leave expensive GPU resources underutilised. For AI pipelines dealing with medium-sized files (over 512 KiB), Azure Premium Files is the go-to solution. It offers the high IOPS and low latency that training and inference tasks demand.
To further enhance data movement, SMB Multichannel creates multiple parallel connections between compute instances and Azure Files. This setup not only speeds up data flow but also ensures reliability - if one connection falters, others keep the process running. For data-heavy operations like loading training datasets or delivering inference results, this can significantly cut job completion times.
Reducing latency is another priority. Positioning virtual machines (VMs) close to storage resources helps, and Proximity Placement Groups (PPGs) take this a step further by physically locating compute and storage within the same datacentre. Additionally, multi-layer caching for frequently accessed data reduces storage calls, saving both time and costs. A well-optimised data pipeline also lays the groundwork for effective monitoring, which is essential for maintaining performance.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting with Azure Monitor
Azure Monitor provides the tools needed to uncover performance bottlenecks across your AI stack. Beyond tracking infrastructure metrics, it’s essential to monitor AI-specific quality signals like model freshness, output accuracy, and response times. These metrics can shift unpredictably due to the inherent variability of AI models.
Centralising all metrics and logs in a single Log Analytics workspace simplifies data correlation. For workloads running on Azure Kubernetes Service, tools like Container insights and Prometheus metrics can help identify performance issues at the cluster level. Meanwhile, Application Insights enables distributed tracing, pinpointing delays across orchestrators and inferencing endpoints.
Set up alerts for issues like availability drops or quality problems (e.g., model drift or latency spikes) to address concerns before they escalate. Insights from the Log Analytics workspace can also flag inefficient queries by tracking compute time, allowing teams to rewrite slow queries for immediate improvements. Collaboration between operations teams and data scientists is key - defining "healthy" performance for each model ensures that monitoring efforts capture model-specific issues, which standard metrics might miss.
Cost Control Strategies for SMBs on Azure
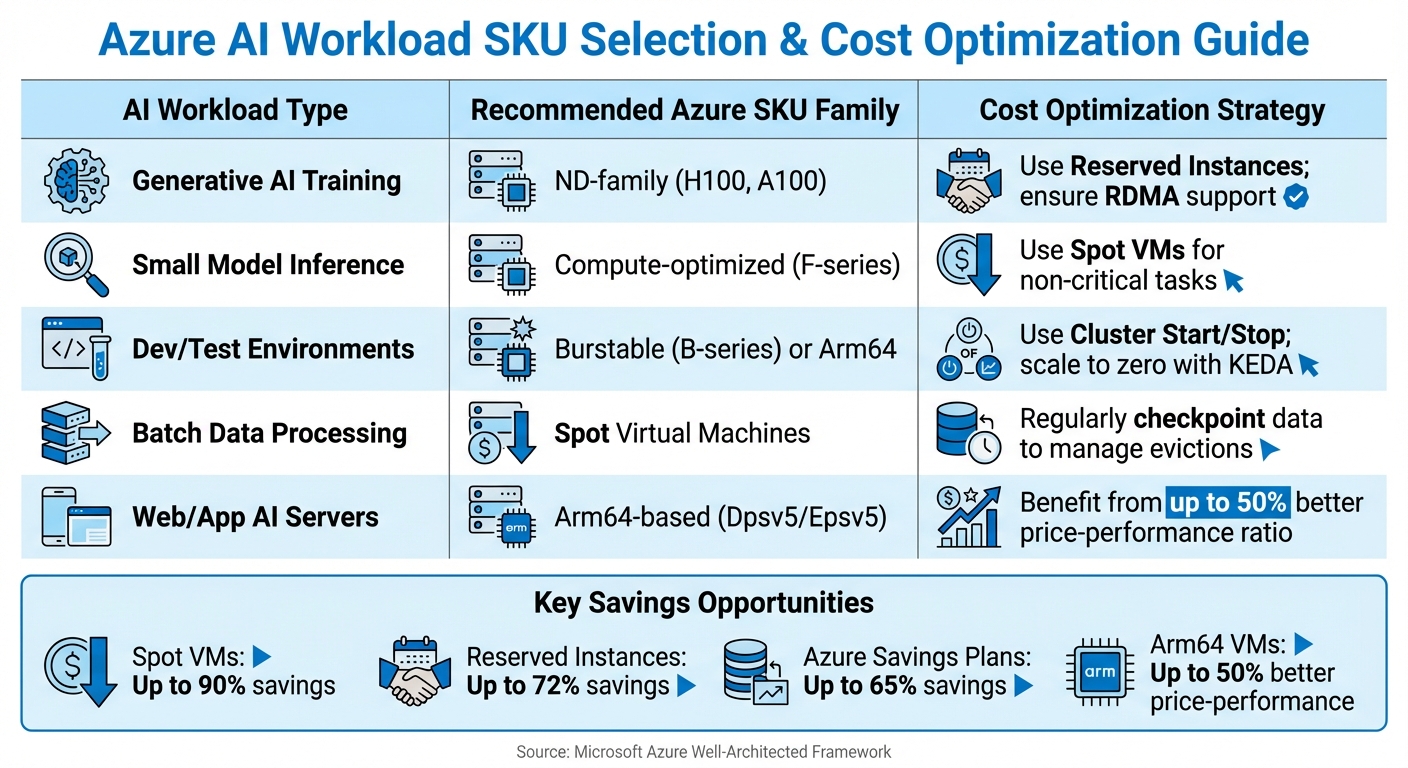
Azure AI Workload Optimization Guide: SKU Selection and Cost Strategies by Use Case
Once you've scaled up, managing costs becomes critical to avoid draining your budget. GPU-heavy training and high-throughput inference can quickly escalate expenses, so it's essential to align resource provisioning with actual workload needs.
Provisioning Models and Matching AI Resources to Workloads
Picking the right provisioning model can significantly reduce your Azure expenses. Spot Virtual Machines are a cost-effective option, offering discounts of up to 90% compared to standard pricing. These are perfect for tasks that can tolerate interruptions, such as batch processing or training jobs that use checkpointing. For workloads that require consistent performance, Reserved Instances offer savings of up to 72% when you commit to one- or three-year plans. If your resource needs vary across VM types or regions, Azure Savings Plans provide up to 65% savings with greater flexibility than reserved instances.
Right-sizing your resources is just as important. Azure Advisor can automatically detect underused resources, suggesting shutdowns for instances where CPU usage drops below 3% or network activity is under 2% for seven consecutive days. For AI workloads with occasional spikes but low average demand, B-series burstable VMs can lower baseline costs while still handling peak performance needs. Additionally, Arm64-based VMs can offer up to 50% better price-to-performance ratios compared to x86 VMs for scale-out workloads.
| AI Workload Type | Recommended Azure SKU Family | Cost Optimisation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Generative AI Training | ND-family (H100, A100) | Use Reserved Instances; ensure RDMA support |
| Small Model Inference | Compute-optimised (F-series) | Use Spot VMs for non-critical tasks |
| Dev/Test Environments | Burstable (B-series) or Arm64 | Use Cluster Start/Stop; scale to zero with KEDA |
| Batch Data Processing | Spot Virtual Machines | Regularly checkpoint data to manage evictions |
| Web/App AI Servers | Arm64-based (Dpsv5/Epsv5) | Benefit from up to 50% better price-performance ratio |
For Kubernetes workloads on AKS, KEDA (Kubernetes Event-driven Autoscaling) can scale resources down to zero when no tasks are queued, ensuring you only pay for active compute time. Pair these strategies with regular cost monitoring to catch overspending early.
Azure Cost Management and Setting Alerts
Monitoring your spending is just as crucial as right-sizing. Azure Cost Management gives you the tools to stay on top of your budget. Set spending limits for each AI project and configure alerts at 50%, 75%, and 90% of your monthly budget. These alerts provide advance warning, allowing you to adjust resource usage or pause less critical workloads.
For more detailed analysis, Azure Advisor samples metrics every 30 seconds and aggregates them into 30-minute windows, helping to identify wasteful spending. For example, it flags VMs for shutdown if CPU usage stays below 2% over three days. Fine-tune your autoscaling thresholds and introduce cooldown periods to avoid unnecessary scaling during short-lived spikes.
Storage costs can also sneak up on you. Use Azure Blob Storage lifecycle policies to automatically transition infrequently accessed training data from the Hot tier to Cool or Archive tiers, significantly reducing storage expenses. Additionally, keeping your compute and data in the same region eliminates costly data egress charges, which can quickly add up for large datasets.
Reference: Azure Optimisation Tips, Costs & Best Practices
For SMBs aiming to sharpen their Azure cost management skills, the Azure Optimisation Tips, Costs & Best Practices blog is a helpful resource. It offers actionable advice on cloud architecture, security, and performance tuning, complementing the cost-saving strategies outlined here. This guide is especially useful for staying updated on Azure's pricing models and uncovering new ways to streamline your AI infrastructure.
Implementation Best Practices for Scaling AI on Azure
To reliably scale AI infrastructure on Azure, it's essential to use infrastructure as code combined with deployment strategies that minimise risk. These methods build on cost-saving and scaling techniques, ensuring smooth and dependable rollouts. By adopting these practices, you can transition scaling strategies into consistent, code-based deployments.
Infrastructure as Code with Azure Resource Manager Templates
Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates let you define your entire AI infrastructure in JSON, ensuring consistent and repeatable deployments. For small and medium-sized businesses, this removes the risks tied to manual configurations and simplifies versioning and auditing. Alternatively, Bicep offers the same functionality but with a more user-friendly syntax.
You can embed autoscaling rules directly in these templates, making sure scaling logic is versioned alongside your infrastructure setup. For ND-family virtual machines, you can automate the selection of DSVM images pre-configured with CUDA and NVIDIA drivers. This ensures all environments, from development to production, maintain the same setup.
To manage AI-specific settings like prompts or model configurations, externalise them following Twelve-Factor principles. This approach allows for updates without requiring redeployment. Store these configurations in version control alongside your templates to link performance metrics with specific deployment versions.
For more complex workloads, consider the Deployment Stamps pattern. This groups related components - like APIs, databases, and models - into a single "stamp" that scales collectively. ARM templates make it easy to deploy identical stamps, each serving different user groups or workloads. To avoid unexpected costs, set a cap on the number of scale units in your autoscaling logic. Be mindful that some resources, such as Azure API Management instances used as gateways, may take up to 45 minutes to scale.
Safe Deployment Patterns: Deployment Stamps and Progressive Rollouts
Once your infrastructure is defined as code, implement safe deployment practices to update services without causing disruptions.
Start by using deployment stamps to create independent infrastructure copies. At least two stamps are recommended to ensure isolation and uninterrupted availability.
Direct traffic through Azure Front Door or API Management, using tenant mappings stored in Cosmos DB. This setup also supports deployment rings, where updates are first released to customers more tolerant of risks before being rolled out to everyone else. Automate this process with tools like Azure Pipelines or GitHub Actions for seamless progressive rollouts across stamps.
For Kubernetes-based workloads on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), the Standard tier allows scaling up to 5,000 nodes and 200,000 pods per cluster. When upgrading clusters with more than 500 nodes, configure a "max surge" of 10% to 20% of the node pool’s capacity to balance speed and avoid workload interruptions. Using ephemeral OS disks in system node pools (e.g., Standard_D16ds_v5 SKUs) can enhance speed and reliability for system pods.
Keep an eye on stamp capacity using Azure Monitor, and automate the deployment of new stamps as usage nears capacity. This proactive approach ensures you’re prepared for demand spikes rather than scrambling to scale at the last minute.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways and Next Steps
Managing AI workloads on Azure involves juggling three main priorities: cost control, performance, and operational ease. For small and medium businesses (SMBs), it's crucial to align compute resources with specific needs. Mid-tier GPUs or CPUs are well-suited for inference tasks, while high-performance ND-family instances should be reserved for demanding training workloads. Leveraging tools like Spot VMs and Azure Reservations can significantly cut costs.
"Cost optimisation ensures that AI projects remain scalable, predictable, and sustainable, balancing innovation with financial responsibility." – Microsoft Foundry Blog
Performance can also be improved by fine-tuning resource allocation. For example, demand management strategies like caching with Azure Front Door or Redis can reduce backend strain, while API throttling helps manage usage spikes. For generative AI tasks, structuring prompts to increase cache hits can lower costs, as Azure OpenAI often charges less - or nothing - for cached tokens. Pairing this with event-driven autoscaling using KEDA ensures resources scale based on message queue length, offering more precise adjustments than traditional CPU-based scaling.
It’s wise to establish guardrails early on. Use Azure Policy to enforce SKU restrictions, set up budget alerts, and differentiate environments with lower-cost SKUs for on-demand needs. Additionally, apply Blob Storage lifecycle policies to archive infrequently accessed data, keeping storage costs in check.
Simplify operations further by adopting Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) solutions like Azure Machine Learning and Azure OpenAI. These services reduce the administrative workload, with options like PTUs for high-volume tasks and consumption-based pricing for fluctuating demands.
For more ways to save money and build efficient architectures tailored to SMBs, check out Azure Optimisation Tips, Costs & Best Practices for expert advice and updates.
FAQs
How can Azure Spot VMs help lower the cost of running AI workloads?
Azure Spot VMs give you access to unused computing capacity at a fraction of the cost - up to 90% cheaper than standard pay-as-you-go rates. These VMs are perfect for AI tasks that aren't time-sensitive or can tolerate interruptions, such as batch processing or training machine learning models. By using Spot VMs, you can significantly cut costs while maintaining performance for less critical workloads.
What are the advantages of using Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) for deploying AI workloads?
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) offers a powerful way to manage and scale resources effectively, making it a great choice for deploying AI workloads. It streamlines container orchestration, allowing you to adapt to changing demands without hassle.
For small and medium-sized businesses, AKS helps improve performance while cutting down on operational complexities. Its seamless integration with Azure’s ecosystem makes tasks like scaling, monitoring, and managing AI applications straightforward, so you can concentrate on developing new ideas instead of worrying about infrastructure.
How does Azure keep AI workloads secure and reliable?
Azure prioritises the security and reliability of AI workloads by adhering to strong best practices. One key element is the use of Azure security baselines, which align services with stringent security standards, safeguarding data, computing power, and network resources. On top of that, Azure incorporates design principles that support seamless scaling, ensuring workloads maintain consistent performance even as demands increase.
For small and medium-sized businesses, Azure provides customised solutions aimed at balancing security, reliability, and cost-efficiency. With these tools and strategies, businesses can expand their AI operations with confidence, knowing they're built on a secure and dependable platform.




